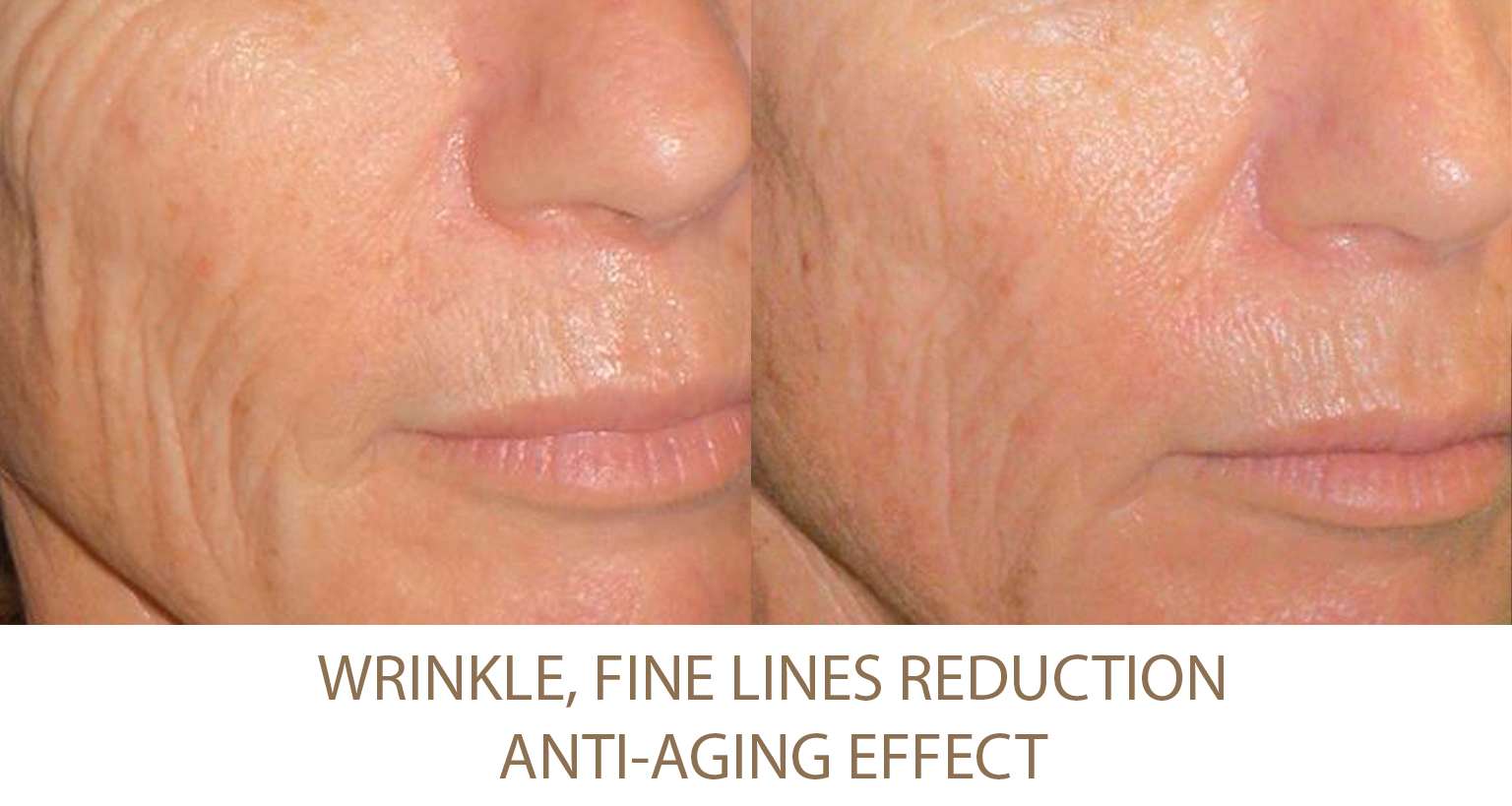
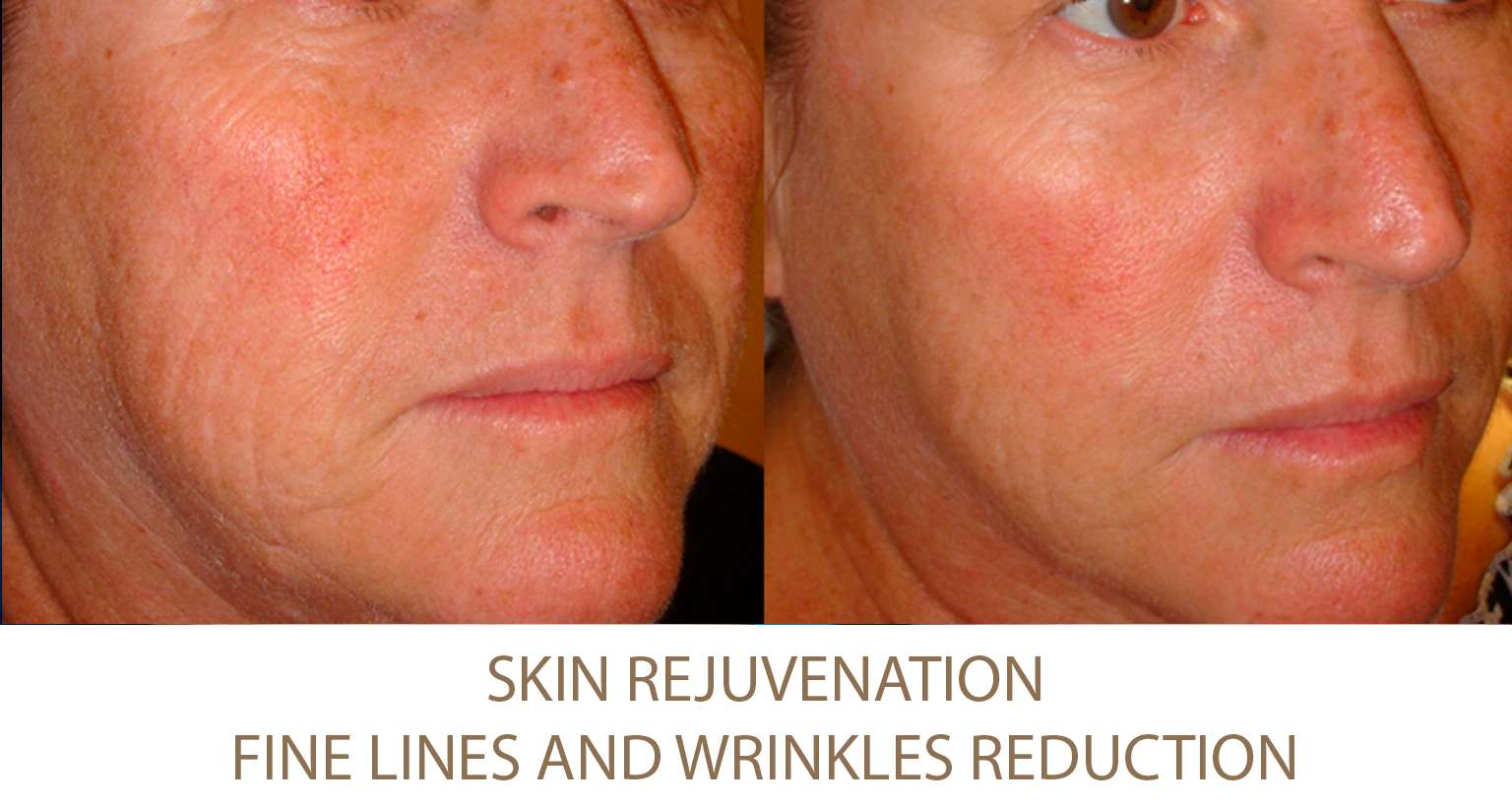
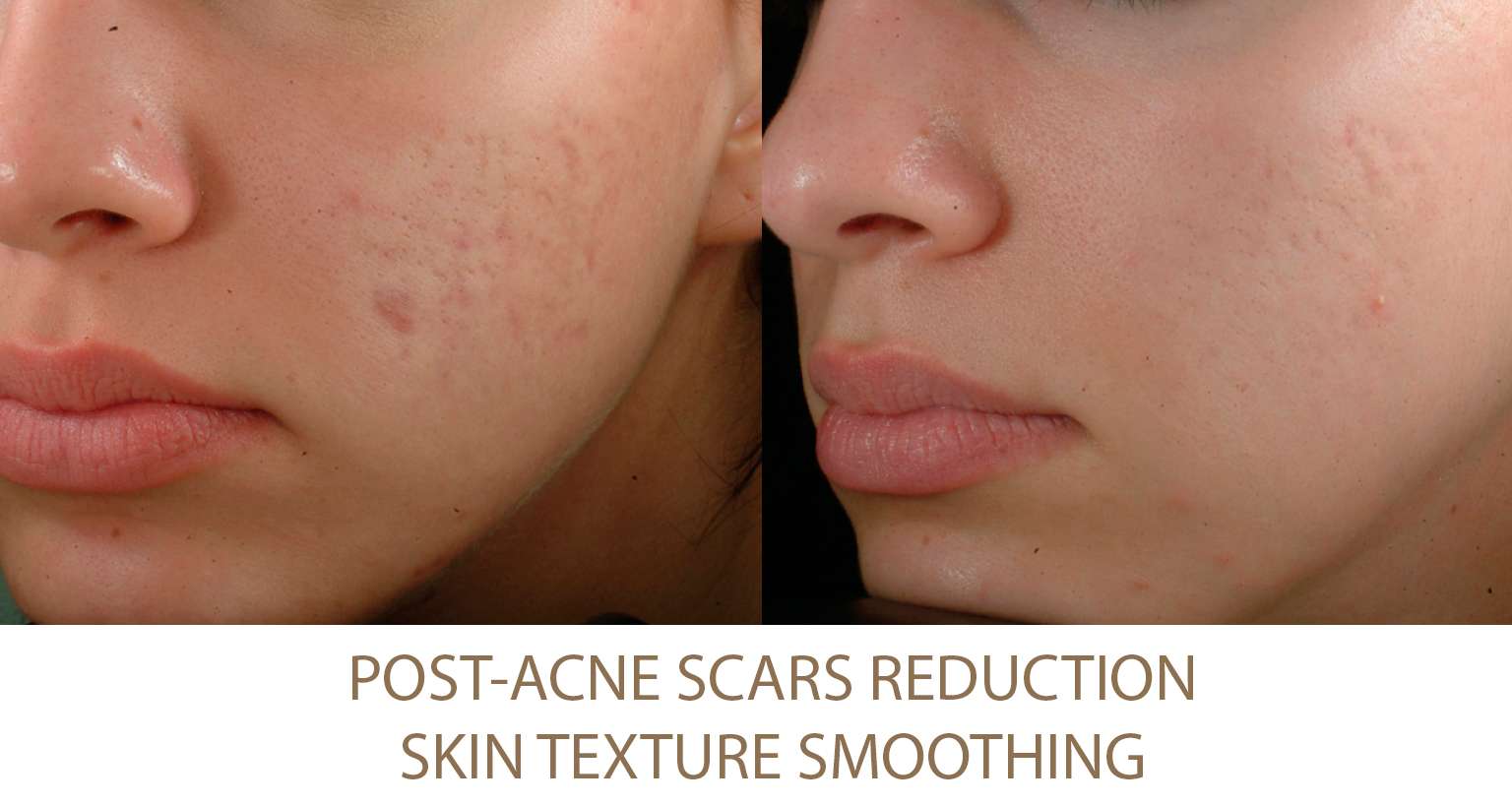
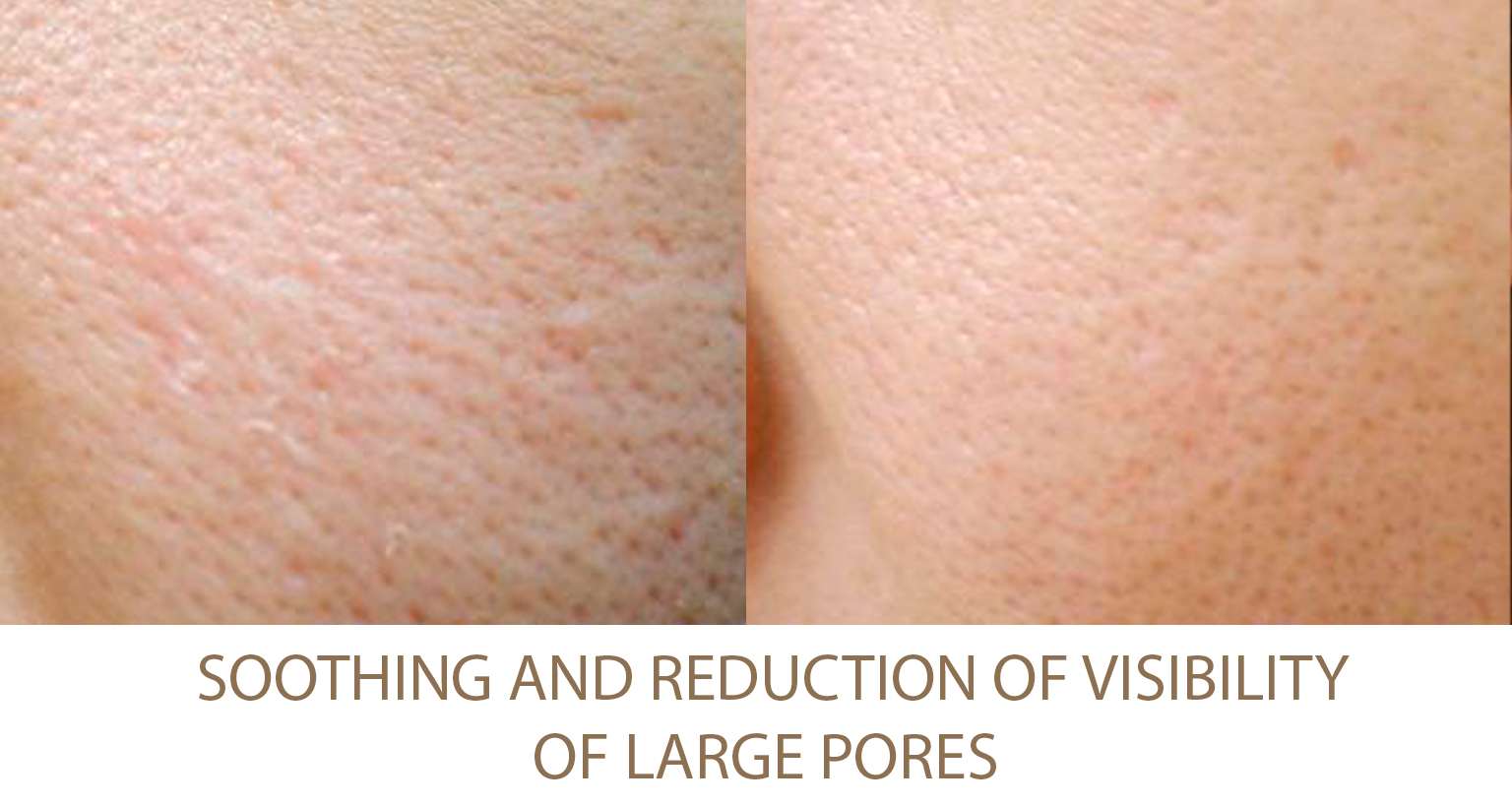
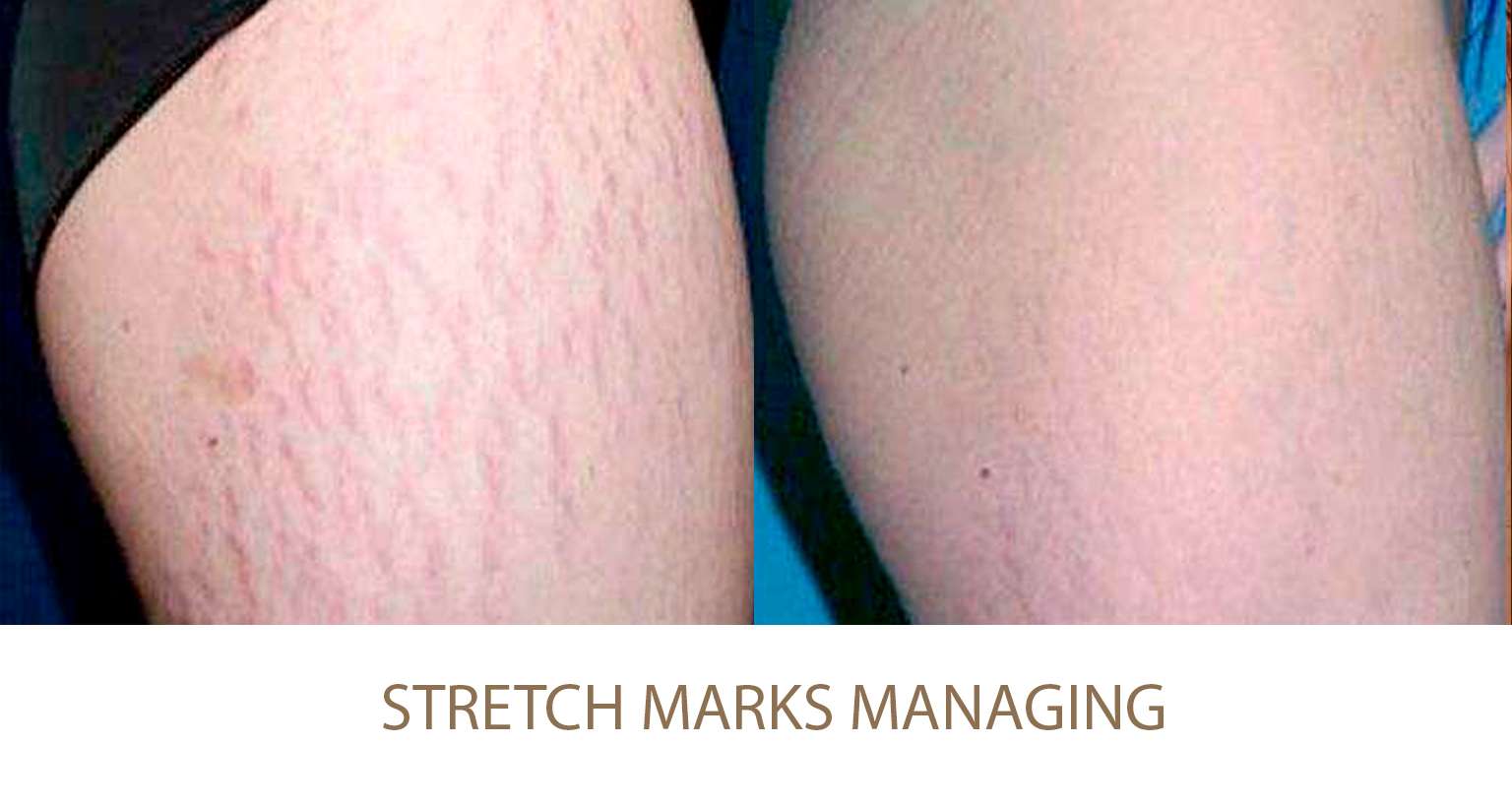
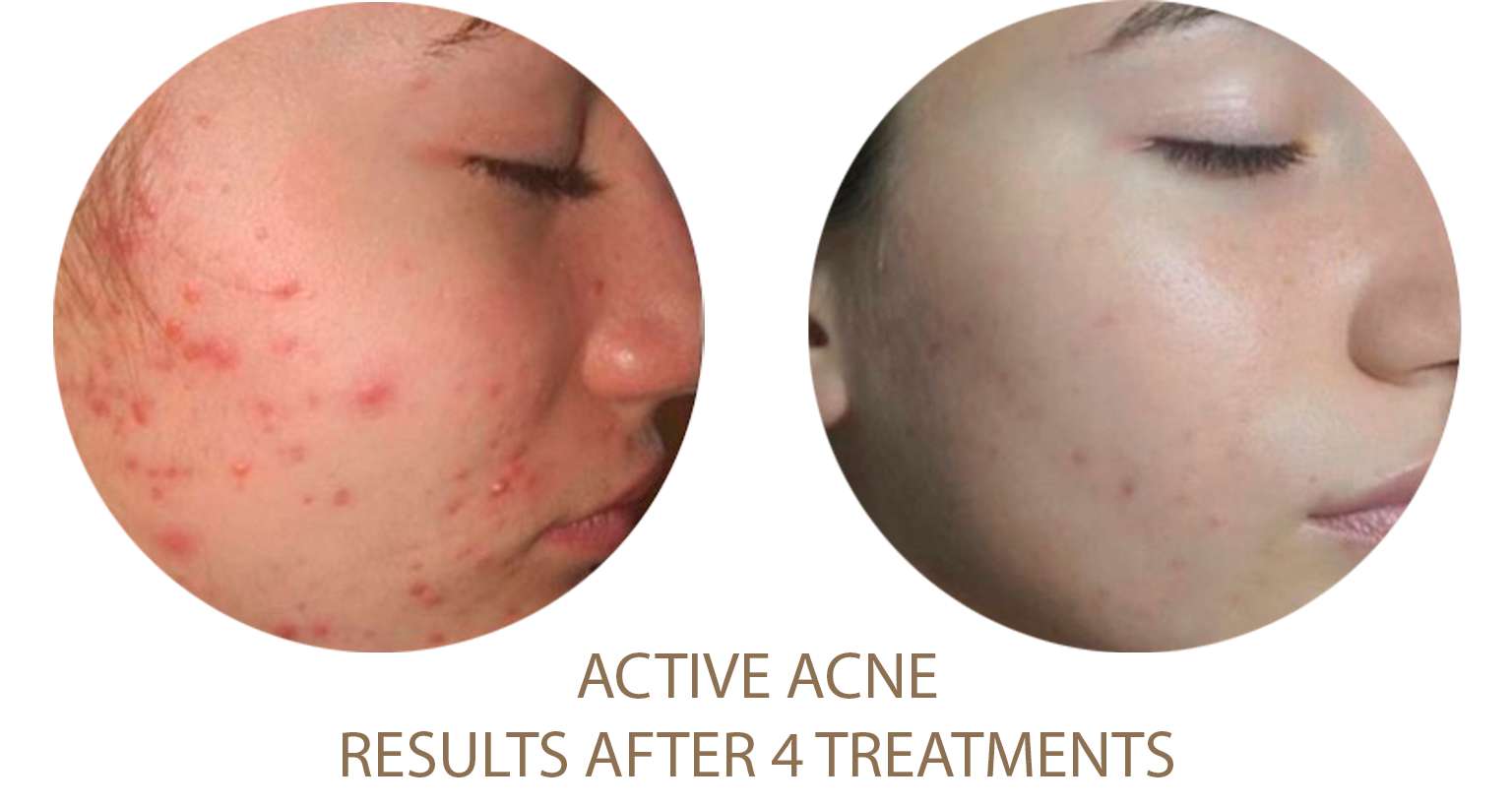
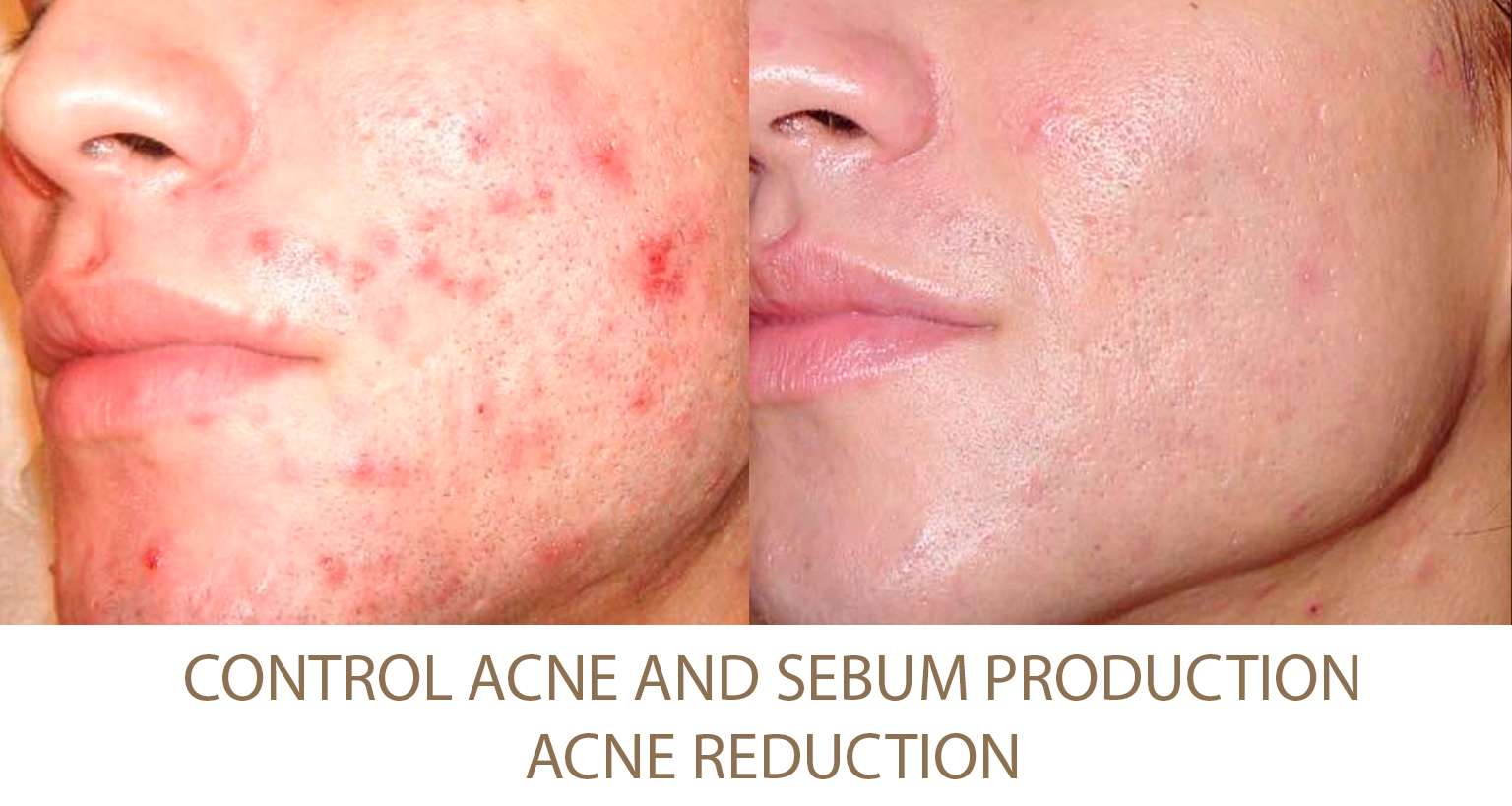
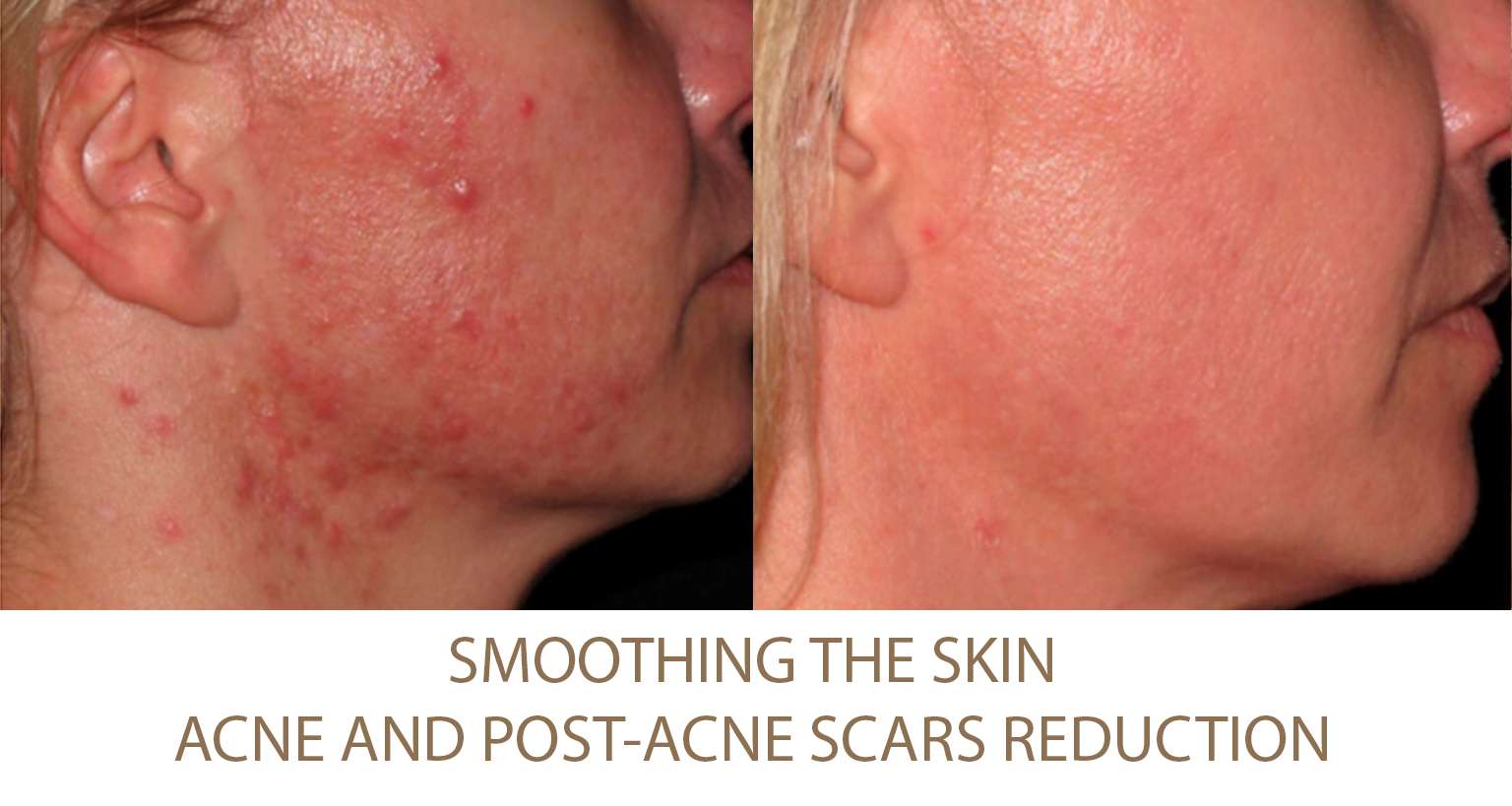
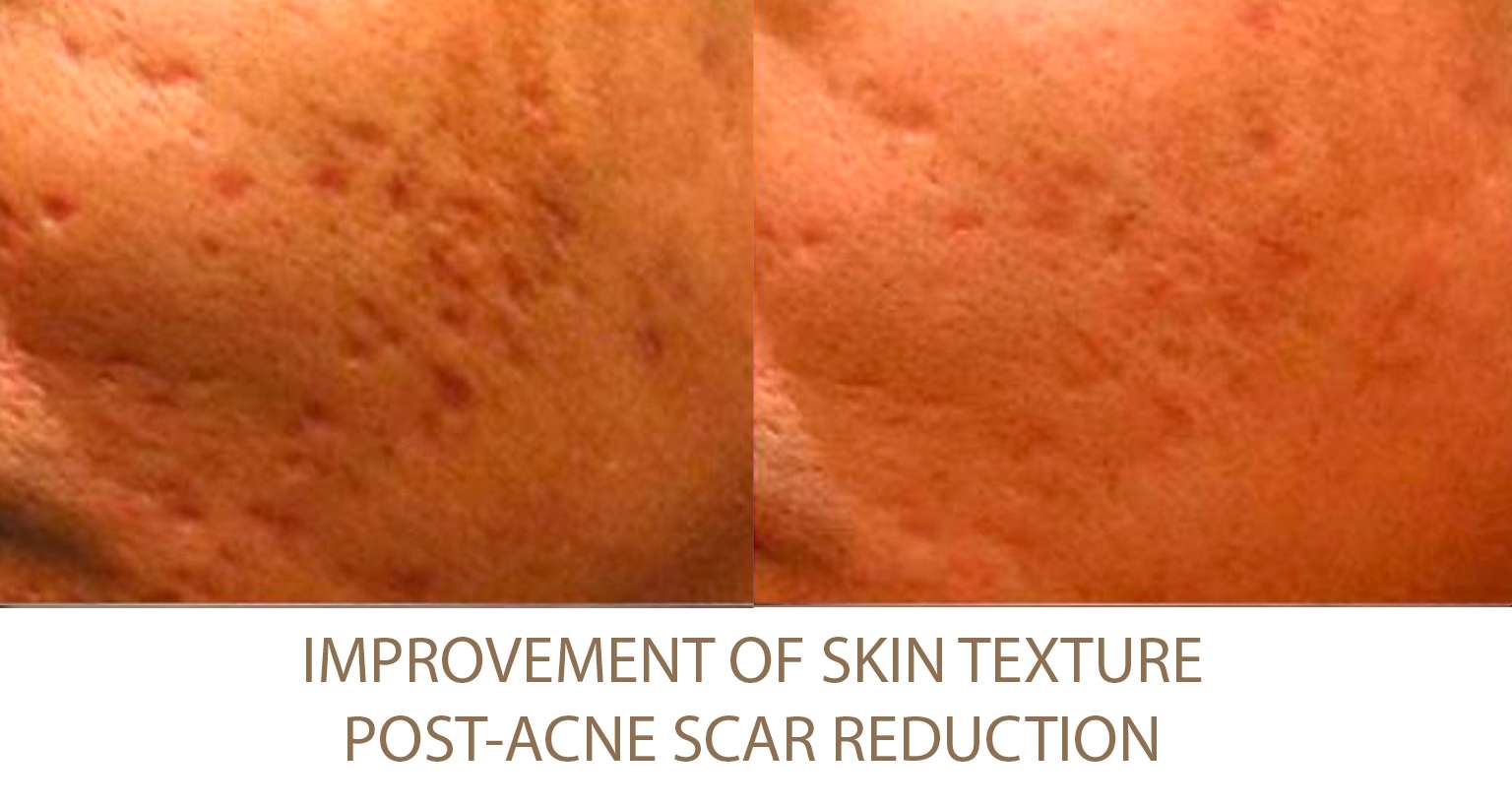
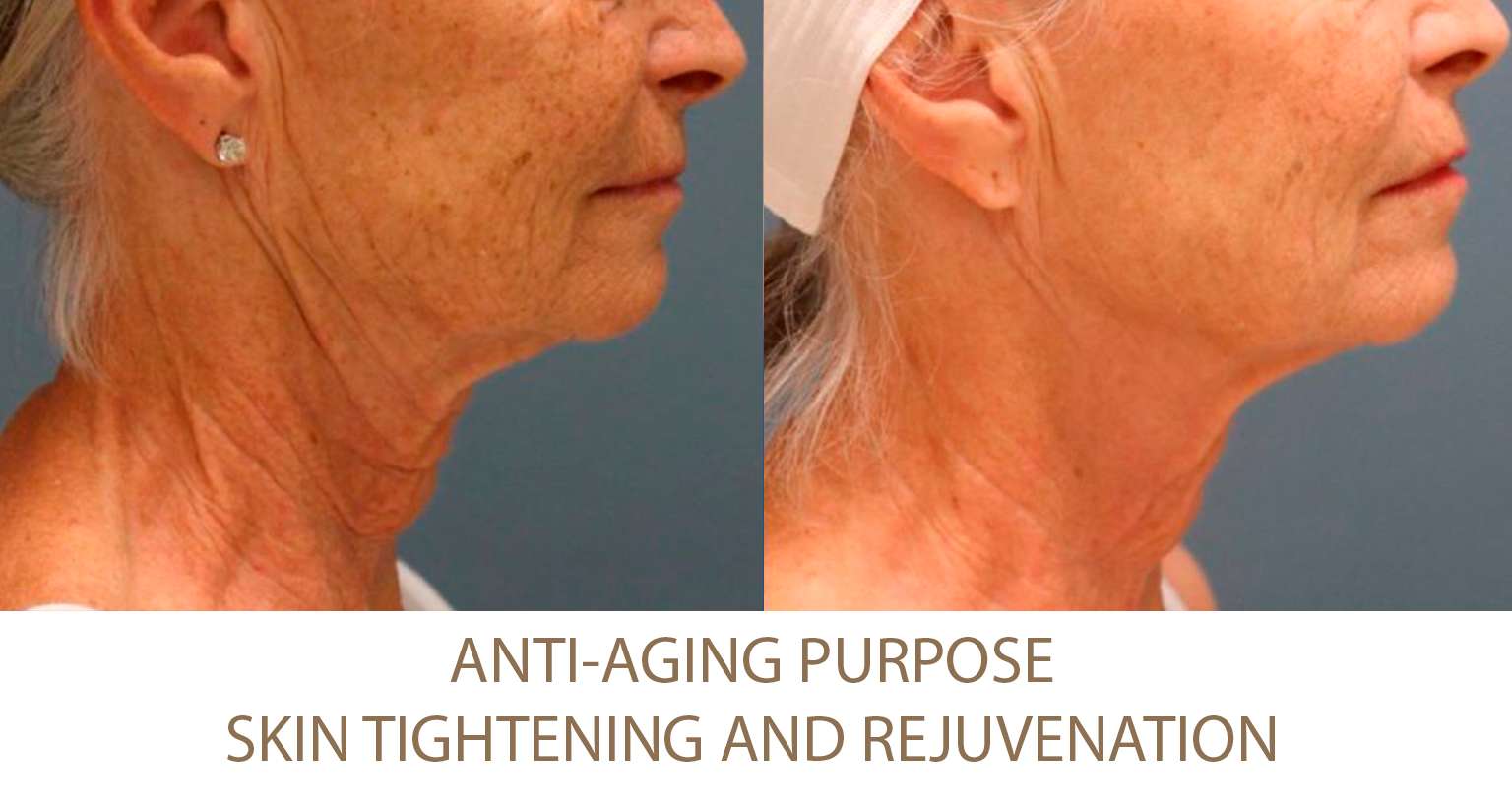
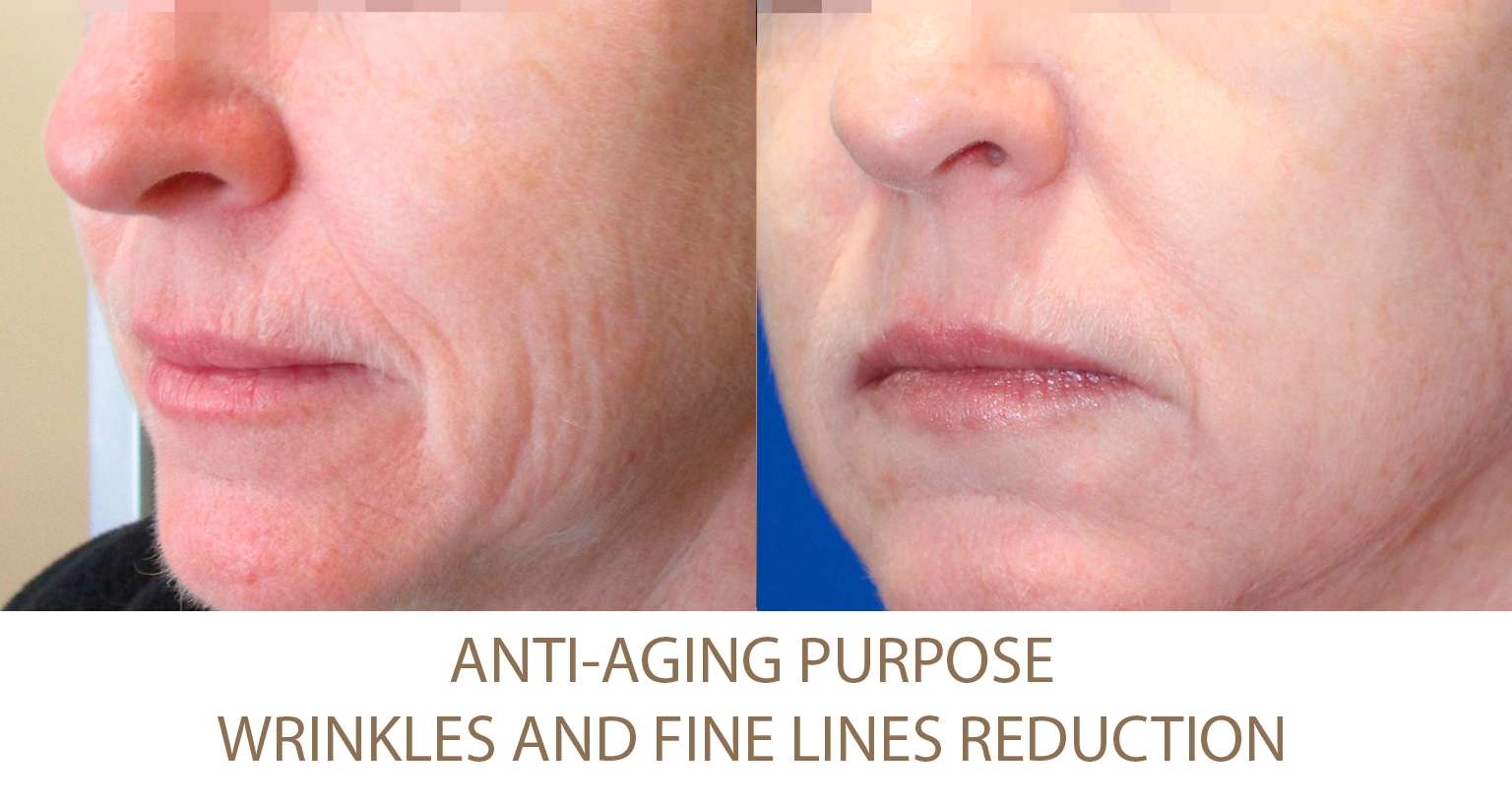
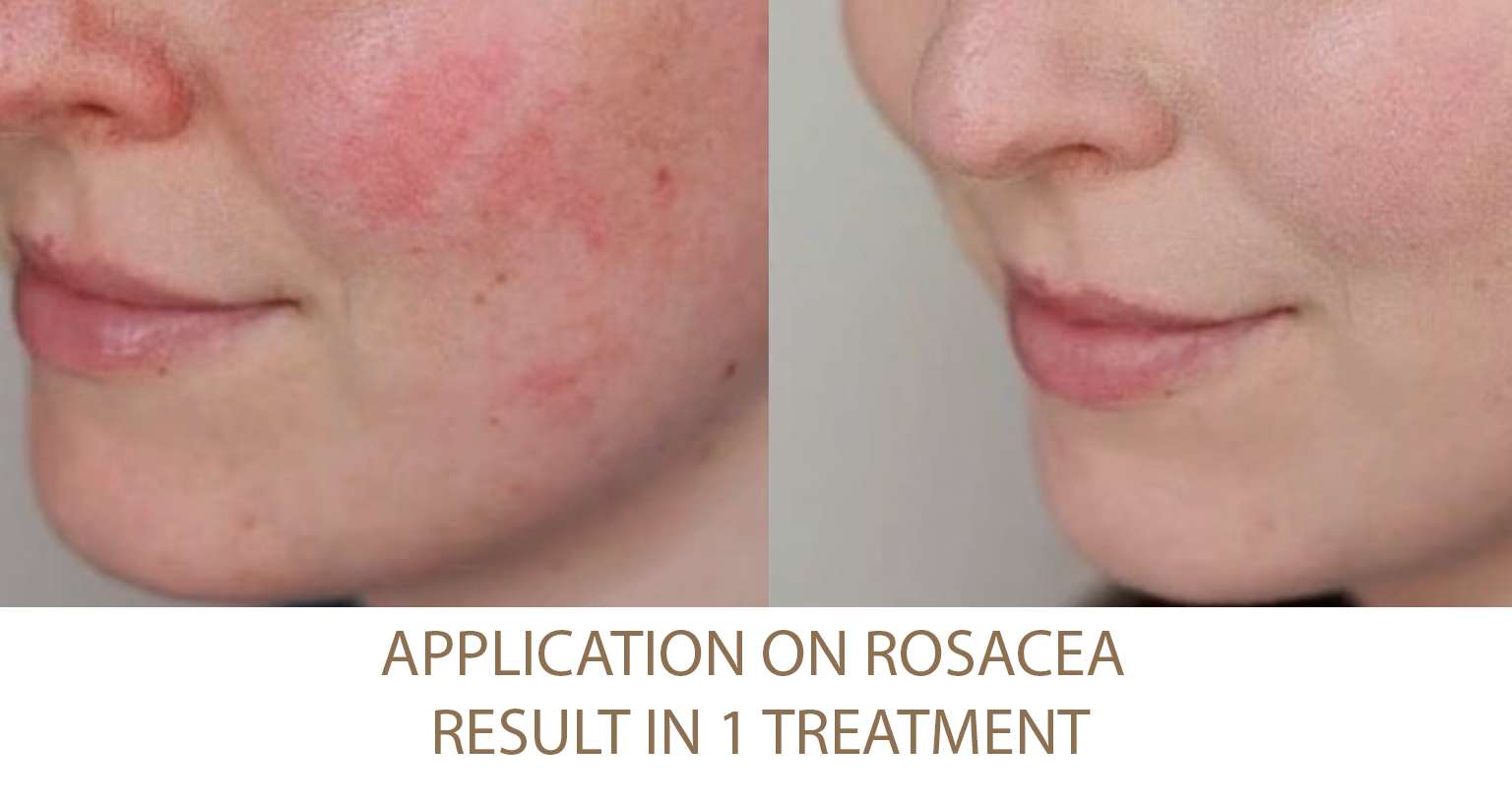
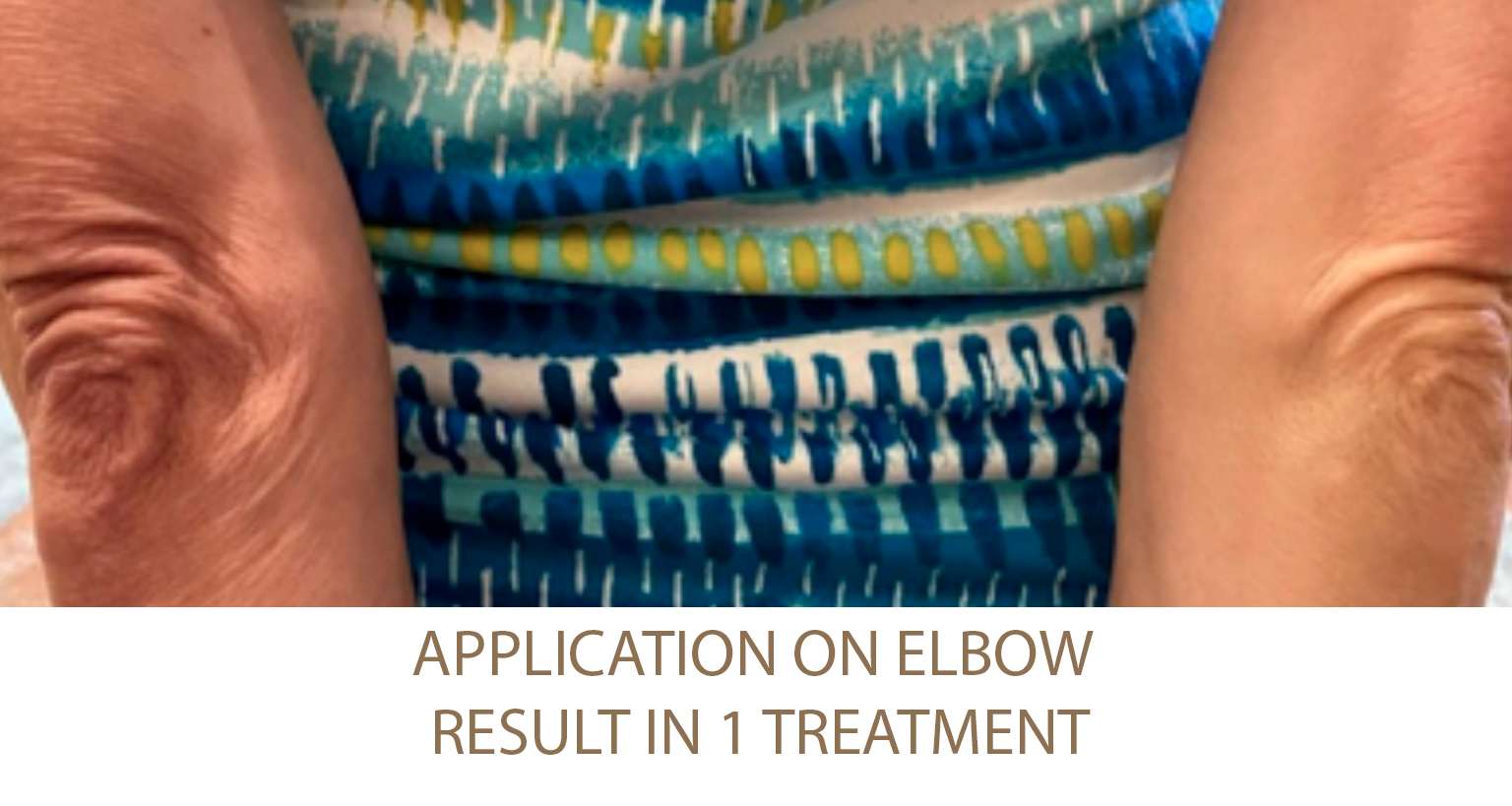
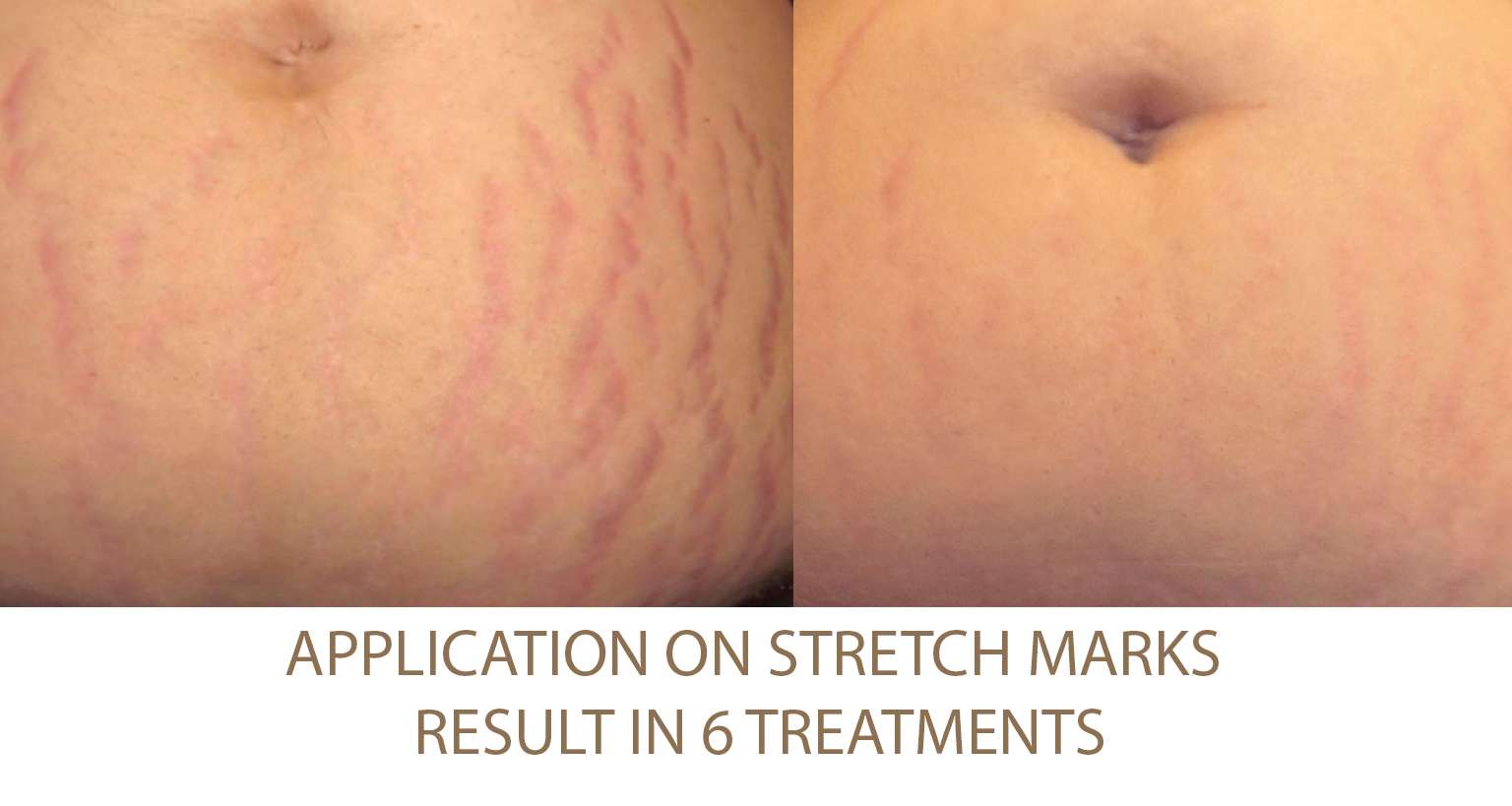
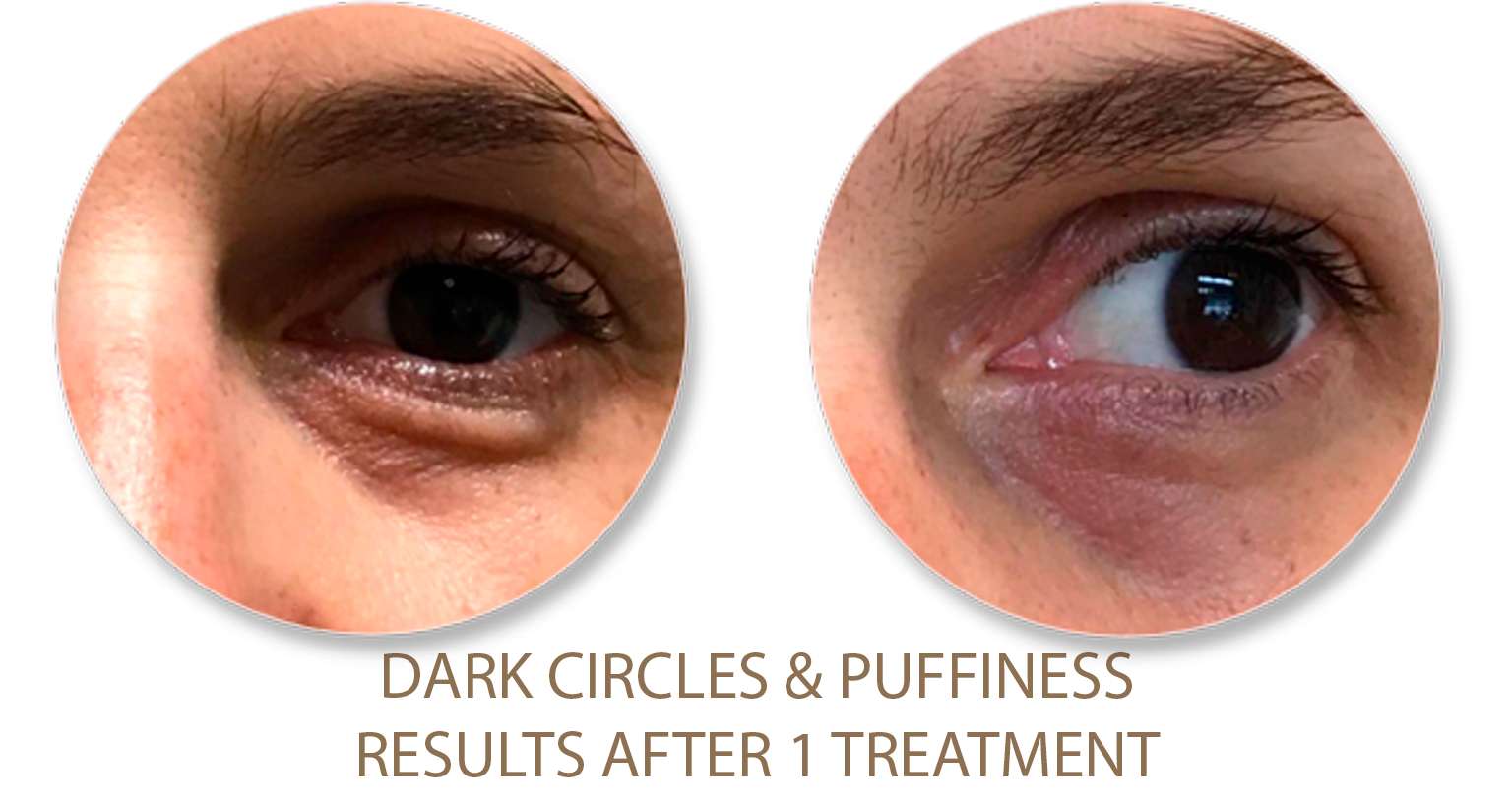
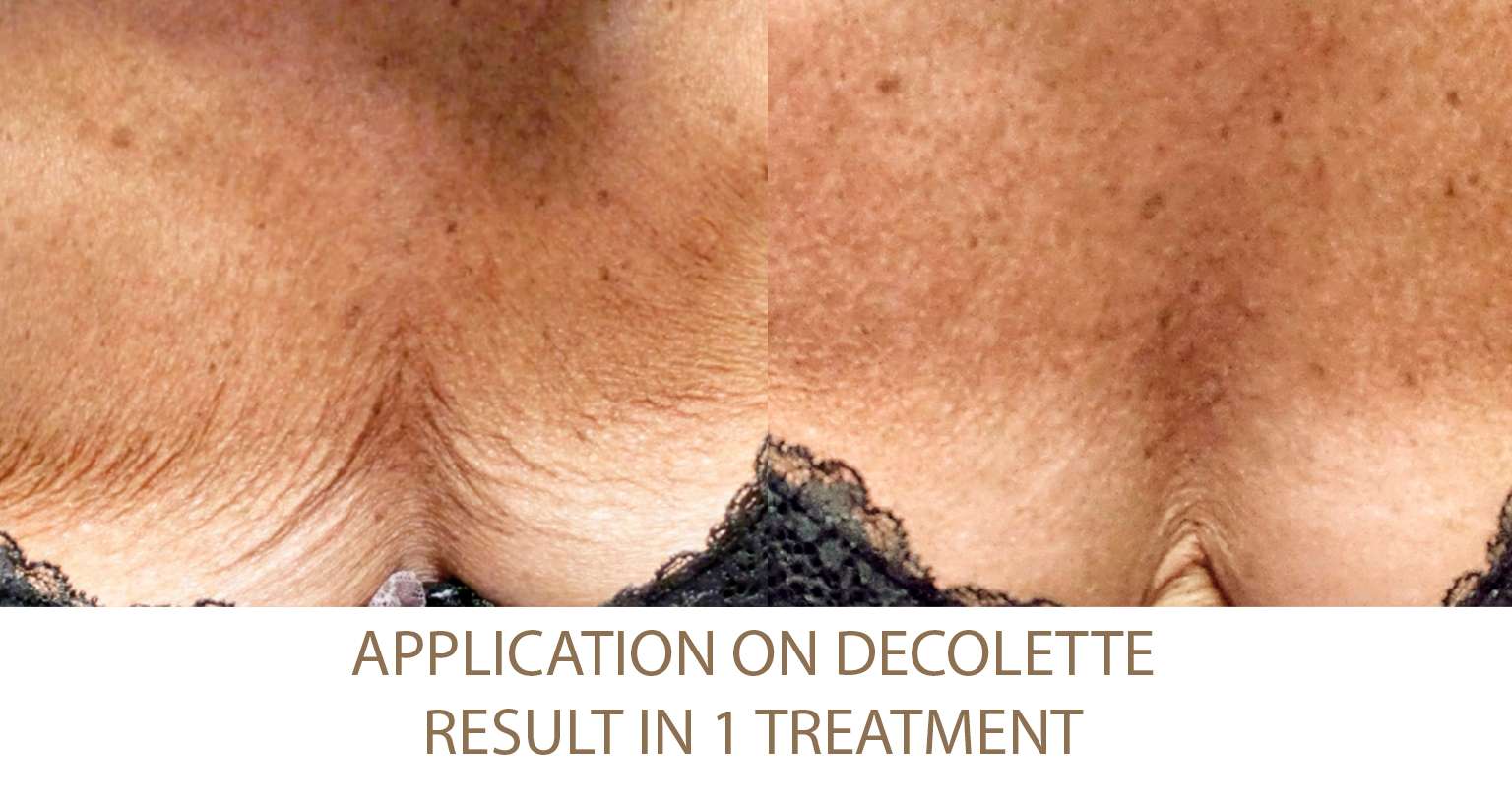
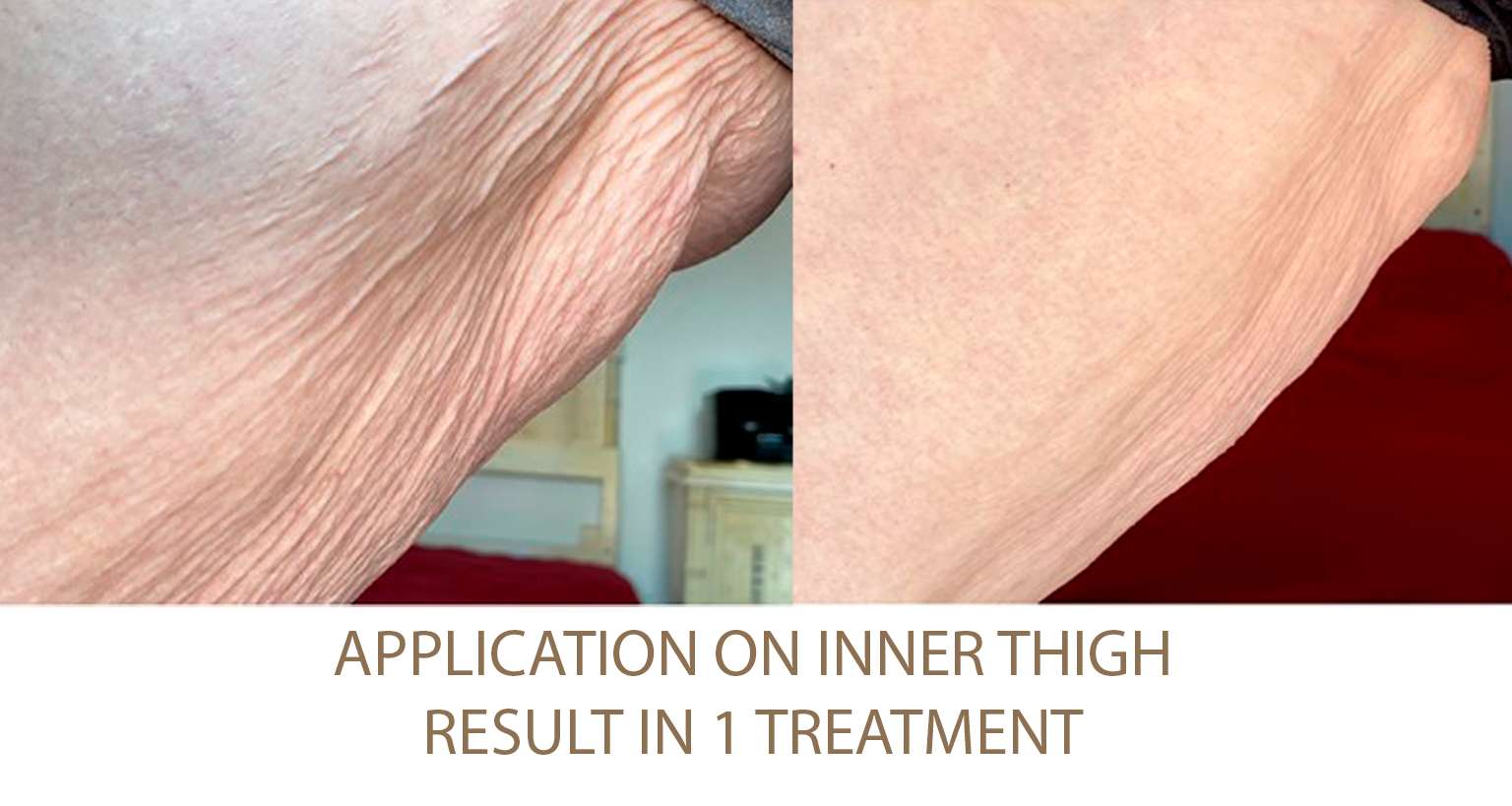
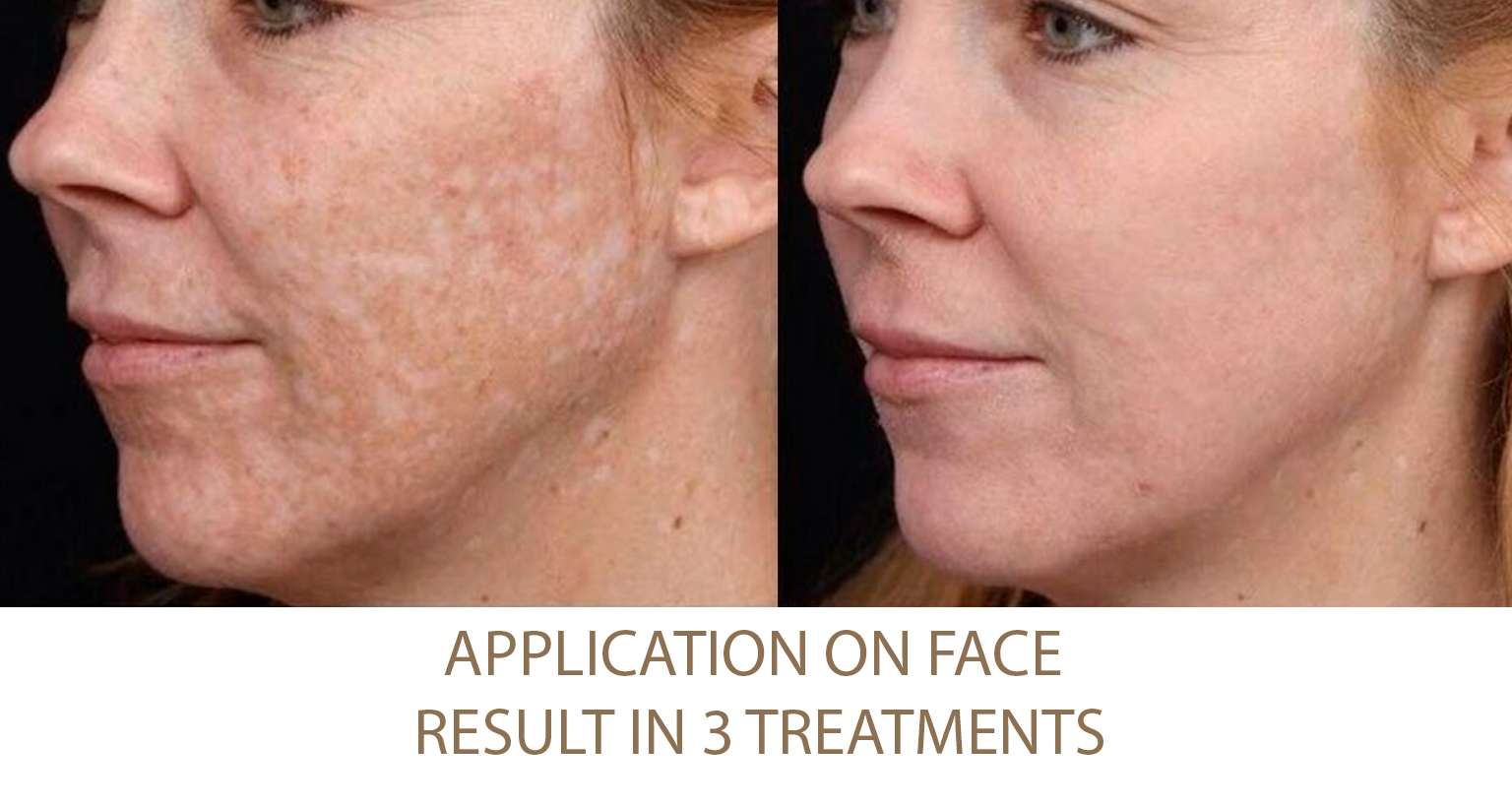
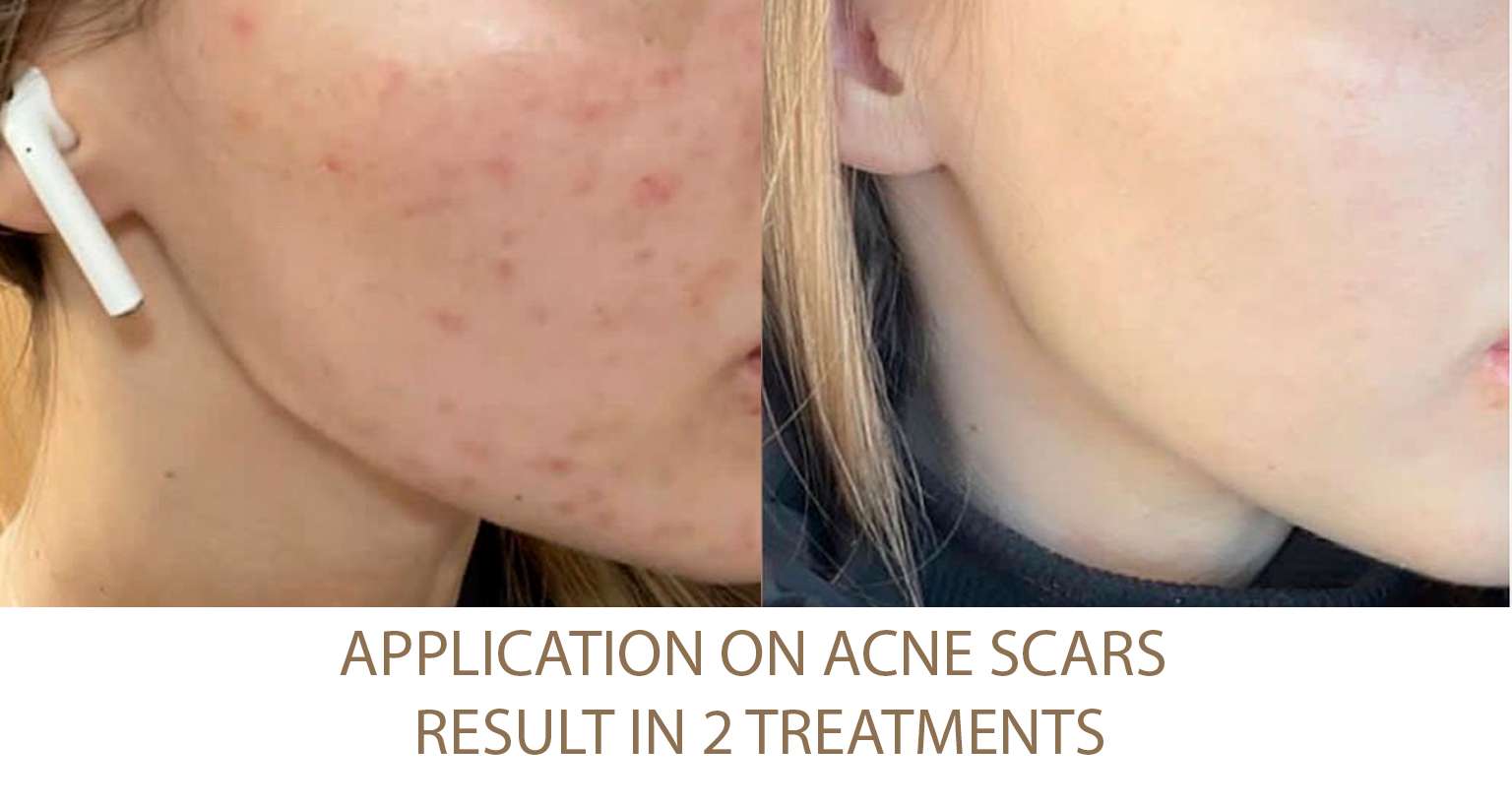
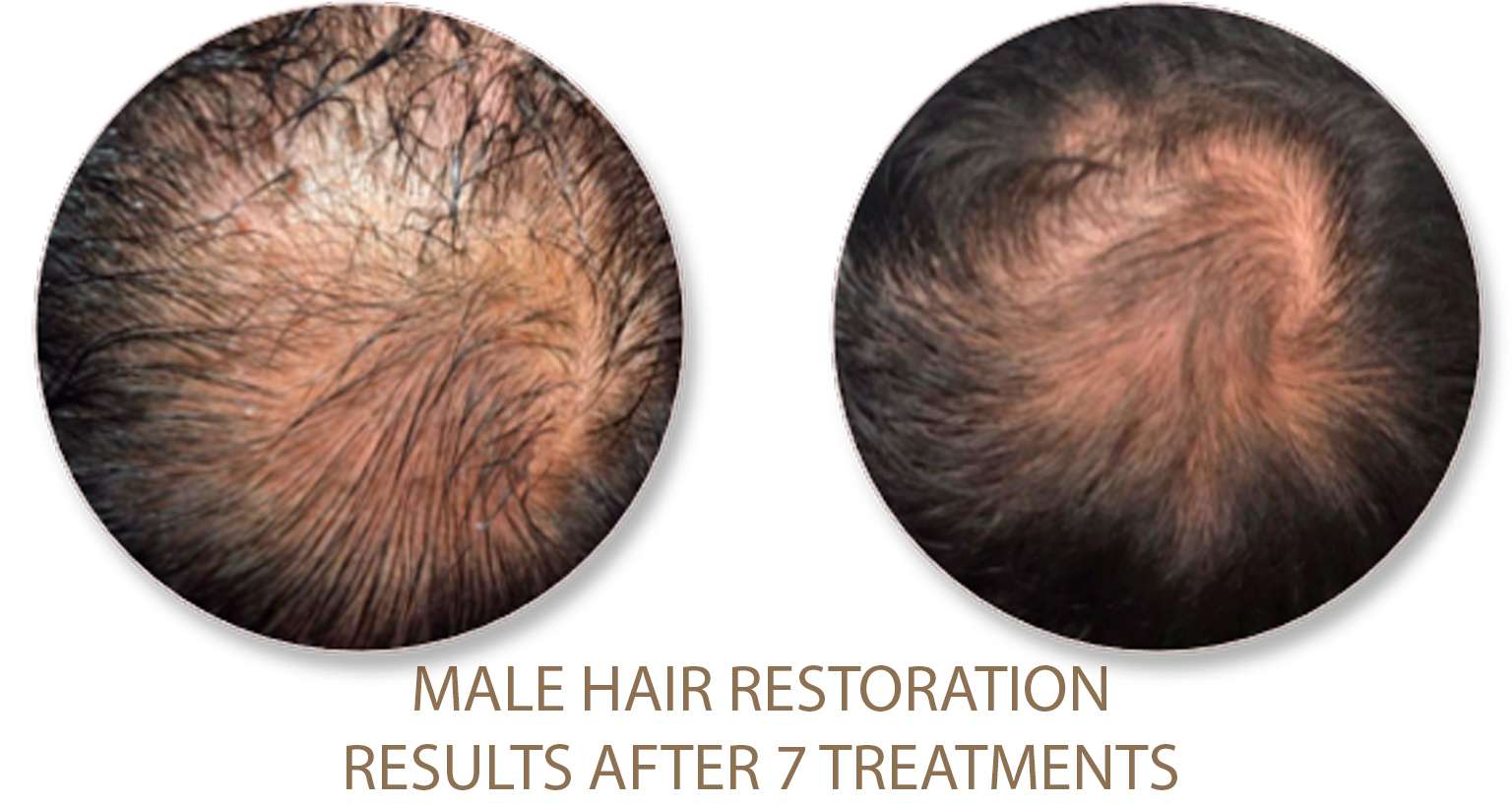
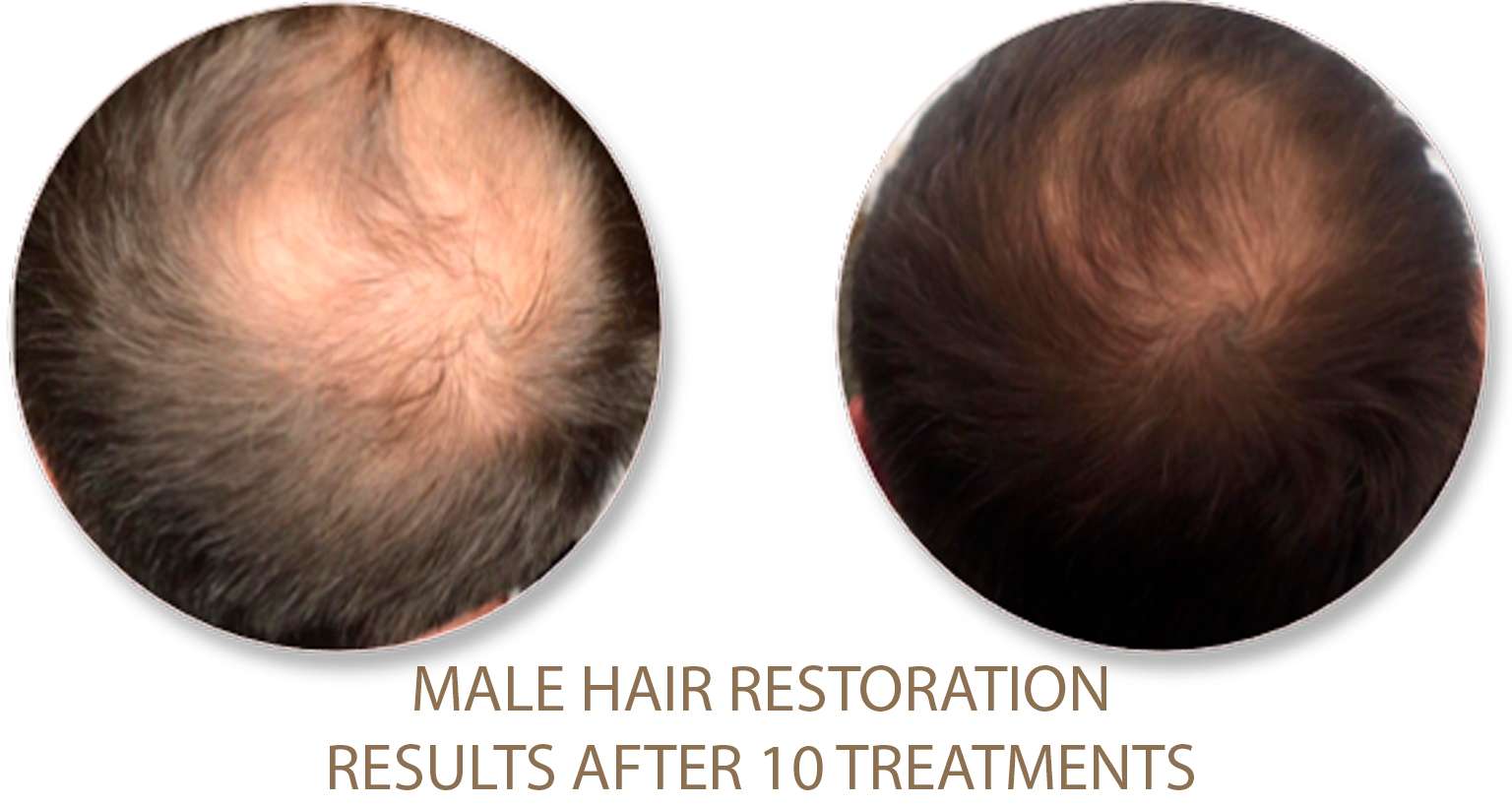
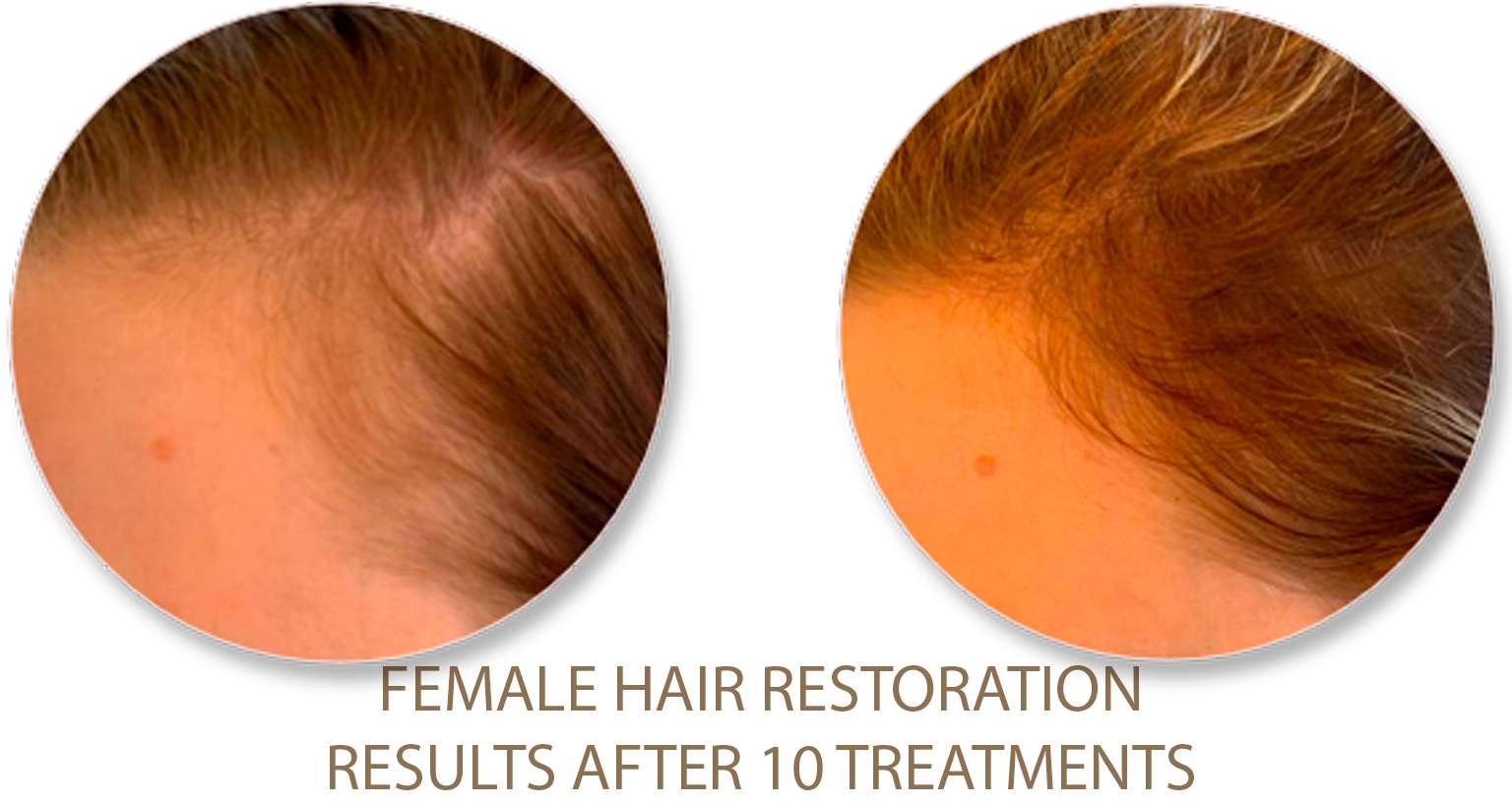
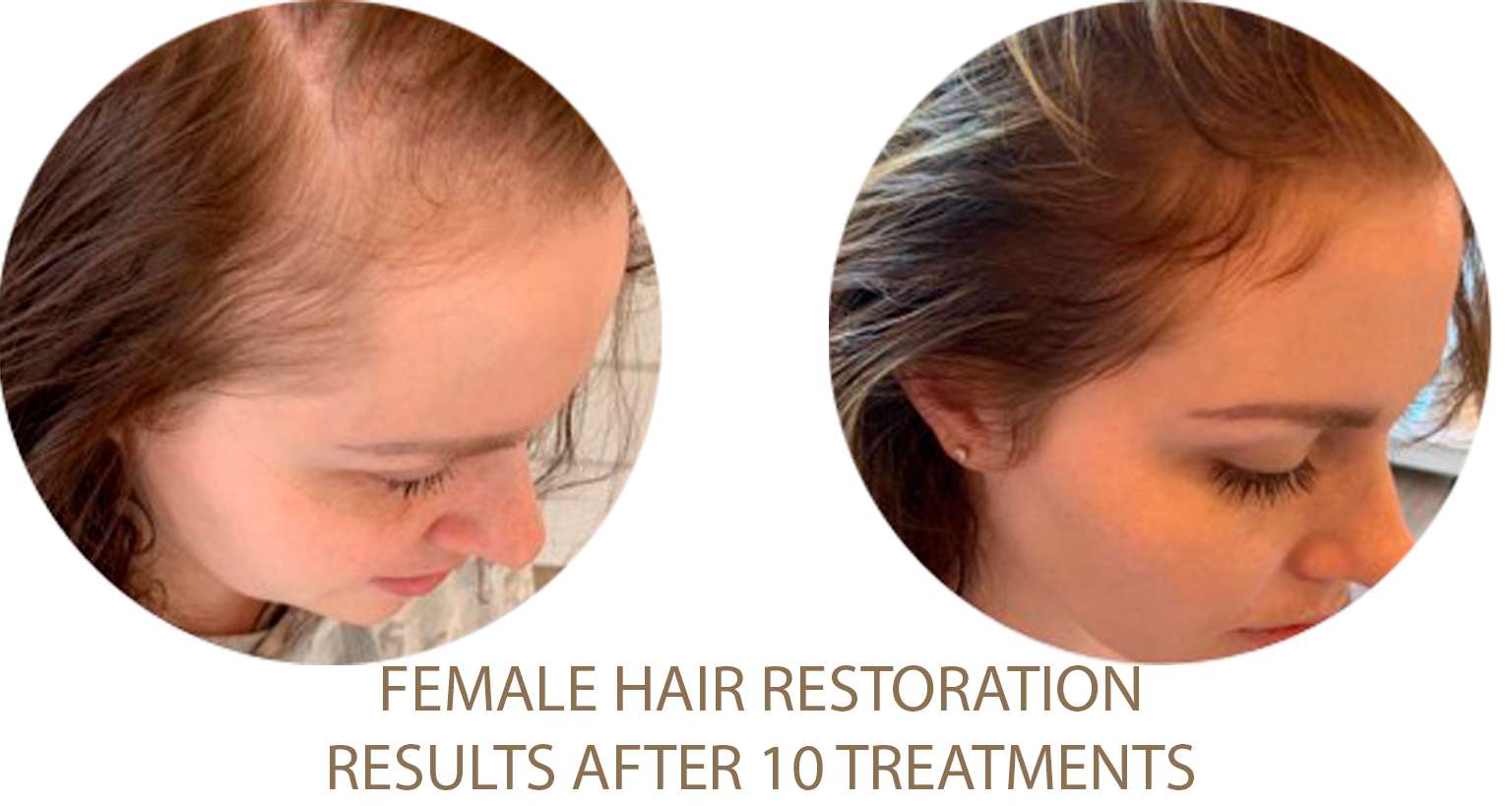
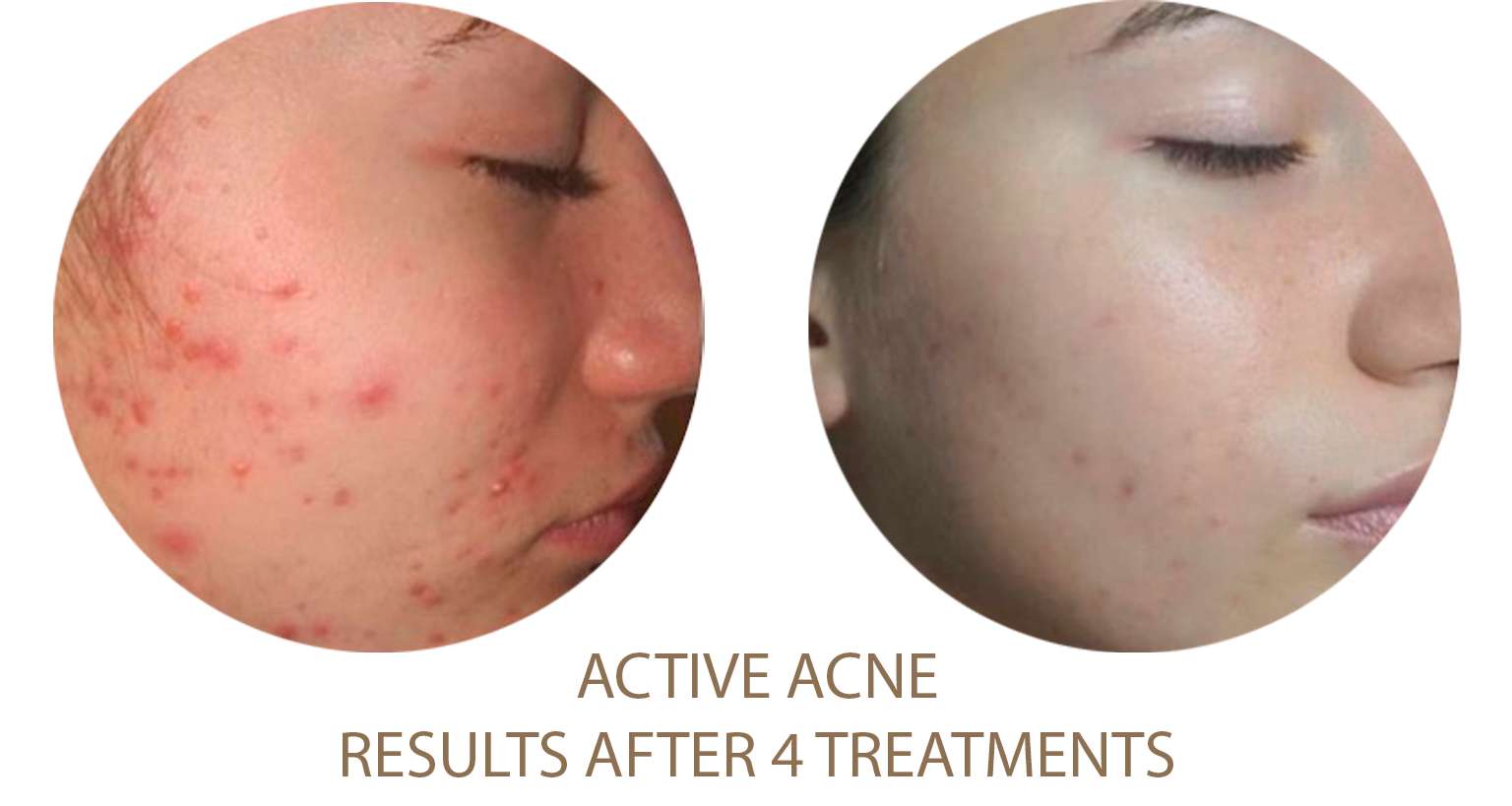
Excessive Fat
An excessive or abnormal accumulation of adipose tissue (body fat) in the body.
While some amount of body fat is essential for various physiological functions, too much fat can have negative implications for health and well-being.
What is Excessive Fat?
When we speak about fat from an esthetic perspective we tend to focus on the fat that sits more closer to the skin. This is called subcutaneous fat and it’s what many people estimate their body fat levels from.
Visceral fat is another type of fat that surrounds all of our organs. This type of fat serves as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease (like high blood pressure), insulin resistance (like diabetes), and high triglyceride and cholesterol levels.
Overweight and obese individuals usually have high levels of both subcutaneous and visceral fat. There is an essential amount of fat all men and women must maintain for homeostasis (appropriate body function), and this number varies by individual.
Men are genetically predisposed to holding fat in their midsections, whereas women are more likely to store fat in their lower body (think hips, buttocks, and thighs).

Treatments for Excessive Fat:
What causes Excessive Fat?
Excessive fat, or obesity, is typically caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Here are some of the main contributing factors:
Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in calories, saturated and trans fats, sugars, and processed foods can lead to weight gain. Frequent consumption of fast food, sugary beverages, and high-calorie snacks can contribute to excessive fat accumulation.
Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles, where individuals engage in little to no physical activity, can lead to weight gain. Regular exercise helps burn calories and maintain a healthy body weight.
Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to gain weight more easily than others. Genetic factors can influence metabolism, fat storage, and appetite regulation.
Environmental Factors: The environment we live in can also impact weight gain. Factors such as easy access to high-calorie foods, portion sizes, and food marketing can influence eating behaviors.
Emotional and Stress Eating: Many people turn to food as a coping mechanism for stress, anxiety, or emotional distress, leading to overeating and weight gain.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions and hormonal imbalances can contribute to weight gain or make it more challenging to lose weight. Examples include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hypothyroidism, and Cushing’s syndrome.
Medications: Some medications, such as certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, and corticosteroids, can lead to weight gain as a side effect.
Lack of Sleep: Poor sleep patterns and inadequate sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and lead to overeating.
Age: Metabolism tends to slow down with age, and people may become less physically active as they get older, making weight management more challenging.
It’s important to note that weight gain is a complex and multifaceted issue, and individual factors can interact differently for each person. In some cases, a combination of these factors may contribute to excessive fat accumulation
Testimonials
What Our Clients Say: